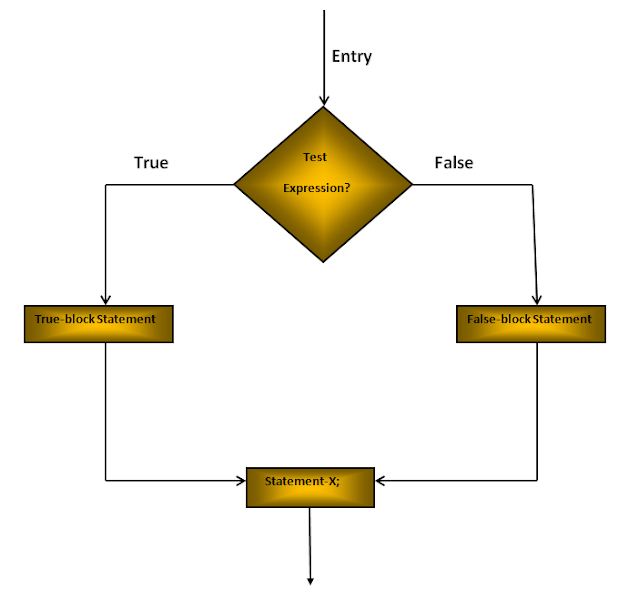
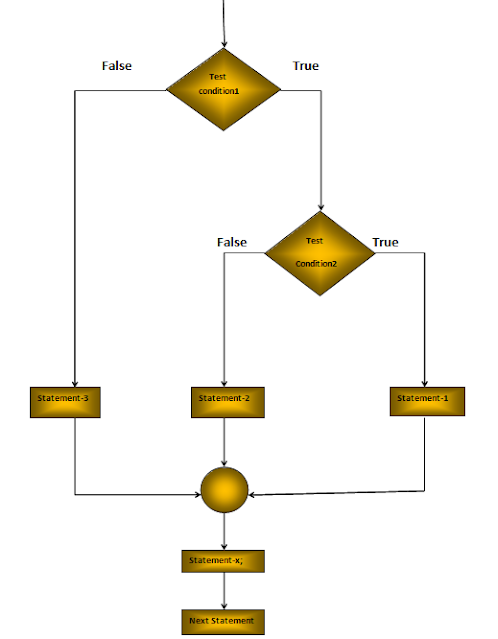
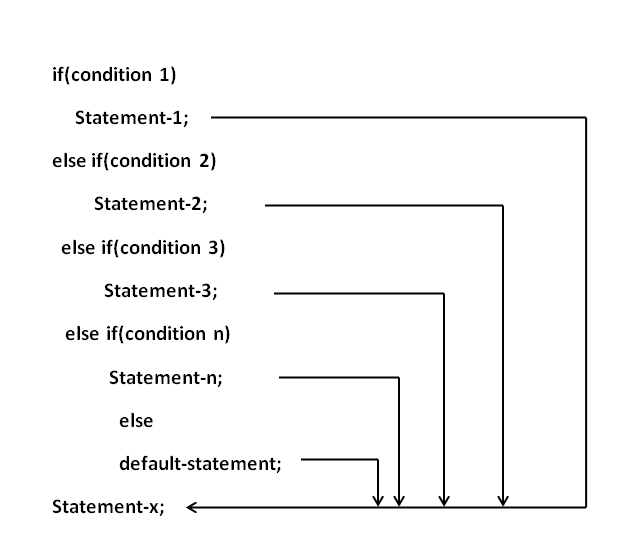
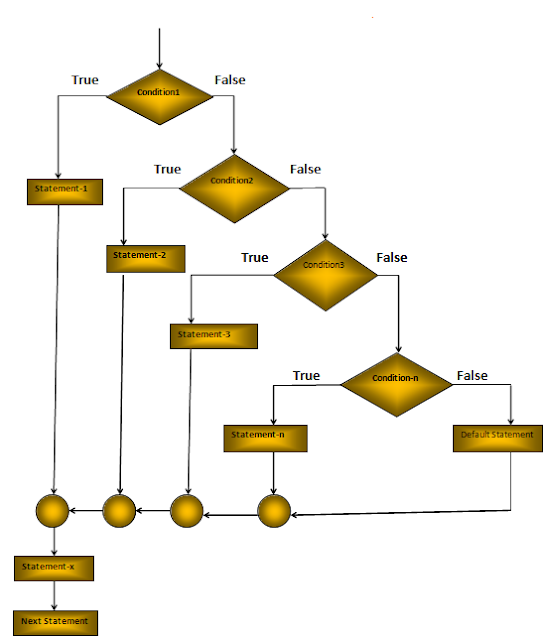
C Data Types: Data types specify the type of data that a variable can store. All C compilers support Five fundamental data types, they are an integer(int), character(char), floating-point(float), double-precision floating-point(double) and void.
There are the following data types in the C language.
| Types | Data Types |
|---|---|
| Primary Data Type | int, char, float, double |
| Derived Data Type | array, pointer, structure, union |
| Enumeration Data Type | enum |
| Void Data Type | void |
Following are the examples of some very commonly used data types used in C:
int: int variable is used to store an integer.char: char stores a single character and requires a single byte of memory in almost all compilers.
float: It is used to store decimal numbers (numbers with floating-point value) with single precision.
double: It is used to store decimal numbers (numbers with floating-point value) with double precision.
Let's see the Primary data types. Its size is given according to 32-bit shown below:
| Data Types | Memory Size | Range |
|---|---|---|
| char | 1 byte(8 bits) | −128 to 127 |
| signed char | 1 byte(8 bits) | −128 to 127 |
| unsigned char | 1 byte(8 bits) | 0 to 255 |
| short | 2 byte(16 bits) | −32,768 to 32,767 |
| signed short | 2 byte(16 bits) | −32,768 to 32,767 |
| unsigned short | 2 byte(16 bits) | 0 to 65,535 |
| int | 2 byte(16 bits) | −32,768 to 32,767 |
| signed int | 2 byte(16 bits) | −32,768 to 32,767 |
| unsigned int | 2 byte(16 bits) | 0 to 65,535 |
| short int | 2 byte(16 bits) | −32,768 to 32,767 |
| signed short int | 2 byte(16 bits) | −32,768 to 32,767 |
| unsigned short int | 2 byte(16 bits) | 0 to 65,535 |
| long int | 4 byte(32 bits) | -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 |
| signed long int | 4 byte(32 bits) | -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 |
| unsigned long int | 4 byte(32 bits) | 0 to 4,294,967,295 |
| float | 4 byte(32 bits) | |
| double | 8 byte(64 bits) | |
| long double | 10 byte(80 bits) |
C Data types Programs:
C Data types program:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include <float.h>
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
printf("Character Bits: %d\n", CHAR_BIT);
printf("Character MAX : %d\n", CHAR_MAX);
printf("Character MIN : %d\n", CHAR_MIN);
printf("Integer MAX : %d\n", INT_MAX);
printf("Integer MIN : %d\n", INT_MIN);
printf("LONG MAX : %ld\n", (long) LONG_MAX);
printf("LONG MIN : %ld\n", (long) LONG_MIN);
printf("SCHAR_MAX : %d\n", SCHAR_MAX);
printf("SCHAR_MIN : %d\n", SCHAR_MIN);
printf("SHRT_MAX : %d\n", SHRT_MAX);
printf("SHRT_MIN : %d\n", SHRT_MIN);
printf("UCHAR_MAX : %d\n", UCHAR_MAX);
printf("UINT_MAX : %u\n", (unsigned int) UINT_MAX);
printf("ULONG_MAX : %lu\n", (unsigned long) ULONG_MAX);
printf("USHRT_MAX : %d\n", (unsigned short) USHRT_MAX);
return 0;
}
Output
Character Bits: 8
Character MAX : 127
Character MIN : -128
Integer MAX : 2147483647
Integer MIN : -2147483648
LONG MAX : 9223372036854775807
LONG MIN : -9223372036854775808
SCHAR_MAX : 127
SCHAR_MIN : -128
SHRT_MAX : 32767
SHRT_MIN : -32768
UCHAR_MAX : 255
UINT_MAX : 4294967295
ULONG_MAX : 18446744073709551615
USHRT_MAX : 65535